Humanoid Robots: Xiaomi’s Factory Revolution in 5 Years
Xiaomi’s Factory Revolution: Humanoid Robots in Five Years
Lei Jun, the visionary CEO of Xiaomi, has set the stage for a manufacturing revolution. His bold claim that humanoid robots will be integrated into Xiaomi factories within the next five years is more than just a prediction; it’s a concrete plan. This move underscores Xiaomi’s commitment to leveraging AI for enhanced efficiency, particularly evident in their electric vehicle factory, and firmly positions the tech giant as a frontrunner in the adoption of advanced robotics. Will this push for automation redefine the future of work?

Lei Jun’s Vision: IA and the Future of Manufacturing
Xiaomi’s success, from dominating the smartphone market (check out the latest Smartphone) to venturing into electric vehicles, is fueled by Lei Jun’s strategic foresight. His statement, “All industries deserve to be reinvented with IA,” highlights the critical role of artificial intelligence in industrial transformation. A prime example is Xiaomi’s EV factory in Beijing. Here, AI-powered vision systems combined with X-rays inspect complex die-cast parts in a mere two seconds. This process achieves five times the precision and ten times the speed of traditional manual inspection. The Xiaomi Car division is pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.
Eliminating Bottlenecks with AI Inspection
This AI-driven inspection addresses a major bottleneck in the manual production of critical components for Xiaomi’s SU7 models. Manual inspection was prone to human error and fatigue. AI not only accelerates the process but also enhances the quality of the final product while reducing defects and operational costs. Jun estimates this automation could unlock a trillion-yuan industrial market.
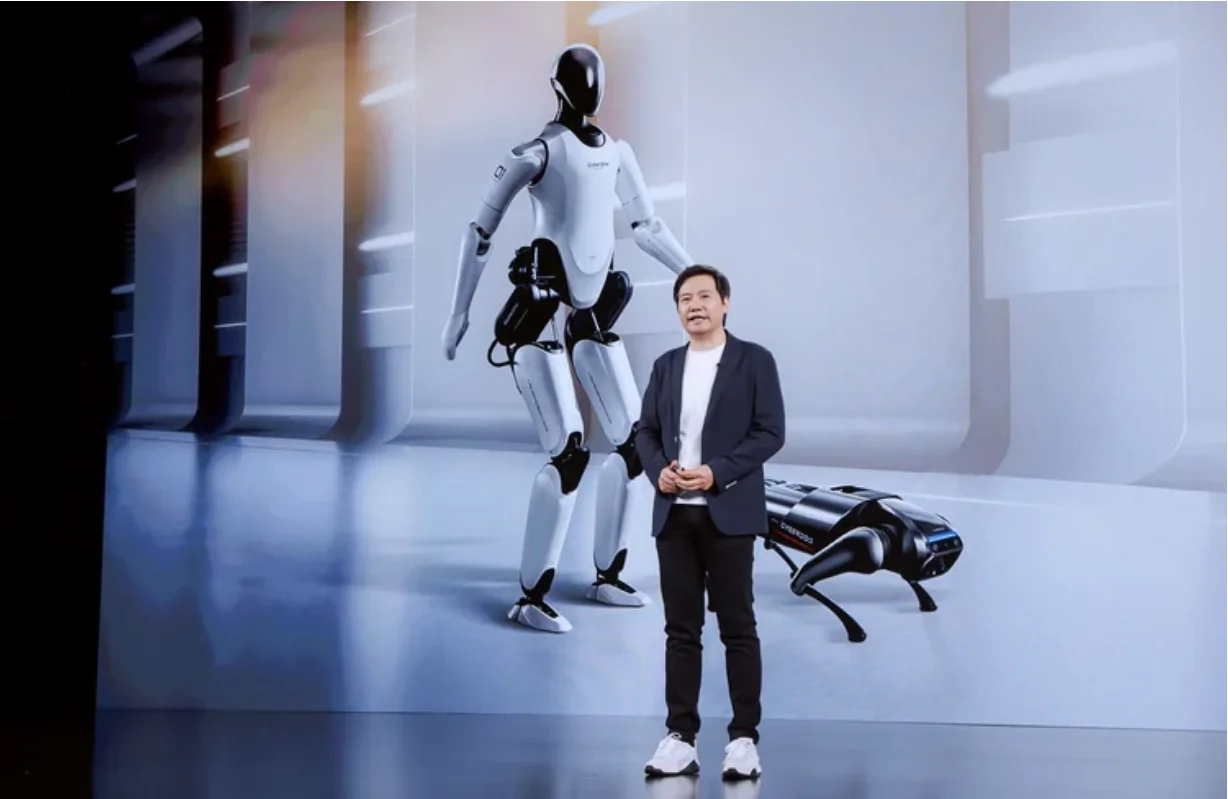
Xiaomi’s Humanoid Robot Ambition: CyberOne
The core of this vision is the deployment of humanoid robots – the next evolution in smart factories. Xiaomi already has robotics experience. In 2022, they unveiled CyberOne, a 1.77-meter-tall, 52kg humanoid robot developed in their Robotics Lab.
CyberOne’s Capabilities
CyberOne isn’t just a prototype. It boasts:
- High-density power actuators for stable bipedal movement.
- Emotional detection (up to 45 classifications).
- 3D environment mapping.
- The ability to walk at 3.6 km/h or run at 7.2 km/h.
While initially focused on emotional interactions, CyberOne now targets industrial applications. Within five years, factories will see a huge transformation thanks to humanoid robots .
Industrial Applications of Humanoid Robots
In Xiaomi’s factories, these robots will handle repetitive, precise, or physically demanding tasks. This includes assembling electronic components and manipulating heavy parts on assembly lines, optimizing workflows, and creating safer environments. To keep up with Xiaomi tech, check out the latest Tech News.
The Factory of the Future: Hyper-Connectivity
Imagine a Xiaomi factory in 2030: Humanoid robots patrol production lines 24/7, working with AI systems to predict and prevent failures. Xiaomi’s Hyper IMP (Intelligent Manufacturing Platform), developed internally and operational in Yizhuang, is the brain behind this operation. This platform proactively solves problems, optimizes processes, and learns autonomously through machine learning.
In 2024, Xiaomi operated fully automated production lines capable of manufacturing 10 million phones annually without human intervention. With HyperOS 3 possibly improving these robotic factories, check the HyperOS 3 Update. Integrating humanoids will amplify this. Workers can focus on high-value roles like engineering, strategic planning, and AI research. Lei Jun envisions a hyper-connected production system where humans and machines coexist in symbiosis.
Implications and Challenges
This large-scale adoption represents a leap towards “Industry 4.0”. China, with its thriving AI ecosystem, aims to lead. Xiaomi’s vertical integration offers a scaling advantage. The industrial robotics market could exceed $200 billion by 2030. However, challenges remain. What happens to assembly line workers? Xiaomi advocates for reskilling, but the transition could create inequalities. Dependence on Chinese AI could also spark security concerns. Xiaomi’s goal is to inspire other companies, such as POCO, and transform the global marketplace.
Lei Jun also foresees humanoid robots in domestic settings, evolving into home assistants for cleaning, cooking, and elder care. This aligns with Xiaomi’s vision of a “future technology ecosystem” with seamless integration.
In five years, Xiaomi’s factories could become living labs for a revolution that redefines work. By balancing efficiency with equity and innovation with ethics, Xiaomi aims to transform its empire and inspire a global industry.